Absorption Spectrum
-
The relationship between the wavelength of light striking a pigment and
how strongly the light is absorbed.
Accessory Oculomotor Nucleus
-
Receives input from the pretectal area, innervates the ciliary ganglion.
Mediates pupillary light reflexes.

Accessory Optic System (AOS)
-
Region of the vertebrate midbrain to which some optic nerve fibers project.
Cells respond to large slowly moving textured patterns and are selective
for both direction and speed of motion suggesting they are involved in
the computation of global motion. Possibly used for the detection of retinal
slip and used in image stabilization. Consists of two sets of retina ganglion
cell fibers and three target nuclei in the anterior portion of the midbrain,
the dorsal, medial and lateral nuclei.
Accidental View
-
A special view of an object in which small perturbations in lighting or
viewing direction drastically change its appearance. For example, imagine
looking at a pencil straight on from the tip. (As opposed to Generic
View).
Accommodation
-
Adjustment of the optics of an eye to keep an object in focus on the retina
as its distance from the eye varies. Process of adjusting the focal length
of a lens.
Acuity
-
The highest spatial frequency rsolvable with a grating of unity contrast
(i.e. the maximum possibly contrast). (Vernier vs. Stereo vs. ?)
Achromatopsia
-
A loss of color vision unaccompanied by attendant loss of other perceptual
functions.
Action Potential
Action Spectra
-
A photoreceptor's relative spectral sensitivity.
Adaptation
-
A change in the sensitivity to light of a photoreceptor or the visual system
as a whole to match the average light intensity present.
Afferent
-
Heading towards. A system's afferent signals are those entering the system
from elsewhere. (As opposed to Efferent)
Affordance
-
(Gibson)
-
A possibility for action afforded to a perceiver by an object. The affordances
of an object depend upon the perceiver as well as upon the characteristics
of the object. For example, a stream affords such actions as jumping and
paddling to a person, but to an frog it affords swimming.
Aftereffect
Afterimage
-
A long lasting change in perceived brightness that occurs after prolonged
viewing of a given luminance that remains after the luminance has been
changed. Presumably due to adaptation in the exposed region.
Aggregate field
-
The area within which the receptive fields of cells in a single hypercolumn
of the visual cortex fall.
Aliasing
-
Results when density of sampling is less than density of signal. One can
only measure the portion of the input falling over the sampled positions.
Sampled values for two different signals can be the same when the in-between
values are different. (See also Nyquist
Limit).

Allelotropia
-
A depth percept can cause a shift in perceived form, namely change in the
perceived distance between patterns in a configuration. For example that
a pattern AB C is viewed in one eye and the pattern A BC is viewed through
the other, the letter B is seen in depth at a position halfway between
A and C.
Amacrine Cell
-
A type of neuron seen in the retina.
Ambient Vision
-
(Ingle, Schneider, Tevarthen, Held 67-68)
-
The role of vision involved in orienting an animal in space and guiding
its larger movements. Sensitive to motion and dependent on peripheral vision.
(As opposed to Focal Vision).
Amblyopia
-
An abnormal development of spatial vision associated with anisometropia
or strabismus in early life.
Visual acuity is reduced in the defocused or deviated eye as a result.
(More Information)
Amodal
-
Perceptually present, but not having a real phenomenological presence.
(As opposed to Modal).
Amodal Completion
-
(Michotte, Tines and Grabbe 1964)
The creation of a subjective contour that is without local
sensory attributes e.g. contrast difference. It is neither a cognitive
inference nor a projection but a direct perception. Seen most often in
displays that have partially occluded objects. (See also Modal Completion).
Anaglyph
-
Device for creating 3-D images using red and blue filters for the two eyes.
Anchoring
-
In any scene, the object which is the lightest is perceived as being white,
or is 'anchored' to white. (Ref. Alan Gilchrist)
Angle of Incidence
-
Angle between an incident ray of light and the perpendicular to a surface.
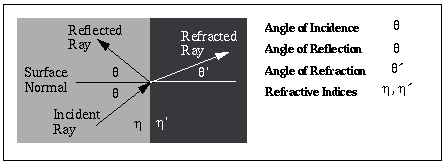
Angle of Reflection
-
Angle between a reflected ray of light and the perpendicular reflecting
surface.
(See Angle of Incidence).
Angle of Refraction
-
Angle between a refracted ray of light and the perpendicular to the refracting
surface.
(See Angle of Incidence).
Anisometropia
-
A disorder involving unequal refractive errors in the two eyes.
Anisotropic
-
Any process or filter which is directionally selective or biased. (As opposed
to Isotropic).
APB
-
(Slaughter & Miller 1981)
-
2-amino-4-phosoponobutyrate. When selectively applied to the mud puppy
retina the On-bipolars, On-amicrines and On-ganglion cells become unresponsive
to light, whereas the Off-cells retain their response properties. Allows
for the study of the Off-cell pathway in isolation. Major finding is that
the center-surround antagonism of Off-center retinal ganglion cells is
not significantly altered suggesting that it is not a product of the interaction
between On and Off cells.
Aperture Problem
-
Any motion detecting device with a field of view which is small relative
to an edge moving through it can only detect the component of velocity
at right angles to the edge, while the component parallel to the edge is
invisible.
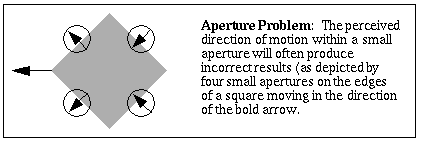
Apparent Motion
-
A observer presented with a display in which two items (lines, dots) in
different locations are alternately exposed at certain interstimulus intervals
will report seeing the item move from the first position to the second
position. Illusion depends on the spatial separation, luminance and duration
of the items. (See also
Transformational Apparent Motion)
Area 17
-
One of Broadman's areas. (See Appendix I: Cortical Areas, V1)
Area 7A
-
Monkey parietal cortex
Area Centralis
-
Area in a vertebrate retina rich in cones, with little pooling of receptor
outputs. In the human eye, the area centralis corresponds to the fovea,
but this in not so in all species.
Area Contrast
-
A contrast effect which is not limited to the borders of an enclosed region.
The change of brightness produced by contrast at the edges of the region
spreads uniformly over the entire enclosed region. (As opposed to Border
Contrast).
Assimilation
-
A neutral pattern of intermediate luminance appears brighter if a superimposed
pattern is made of high luminance lines, yet darker if the pattern consists
of low luminance lines. This effect is in the opposite direction as is
seen in simultaneous contrast.

Automatic Gain Control
-
A fast gain control that aims to a constant output by changing gain in
proportion to signal strength
Auto-Stereogram
-
Unlike classical Random Dot Stereograms (RDS Ref) which require two separate
images presented dichoptically, an autostereogram consists of just one
images viewed by two eyes simultaneously. A depth percept is attained from
this image.